Breast Surgery
Breast augmentation
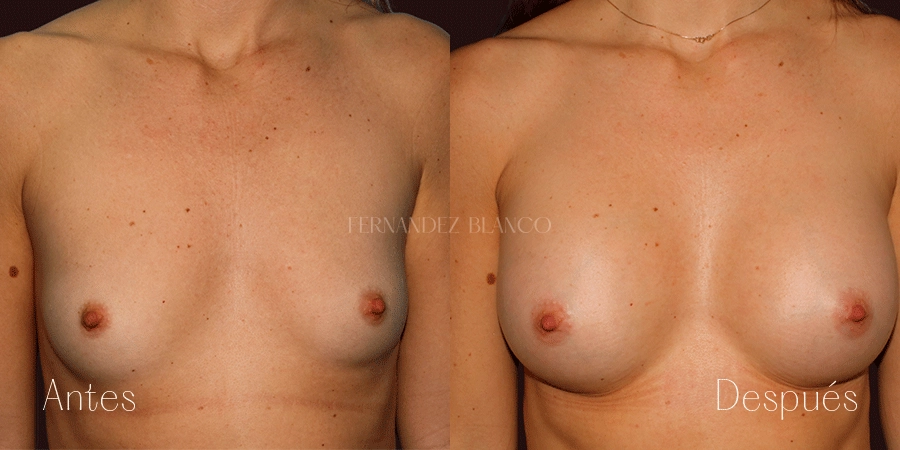
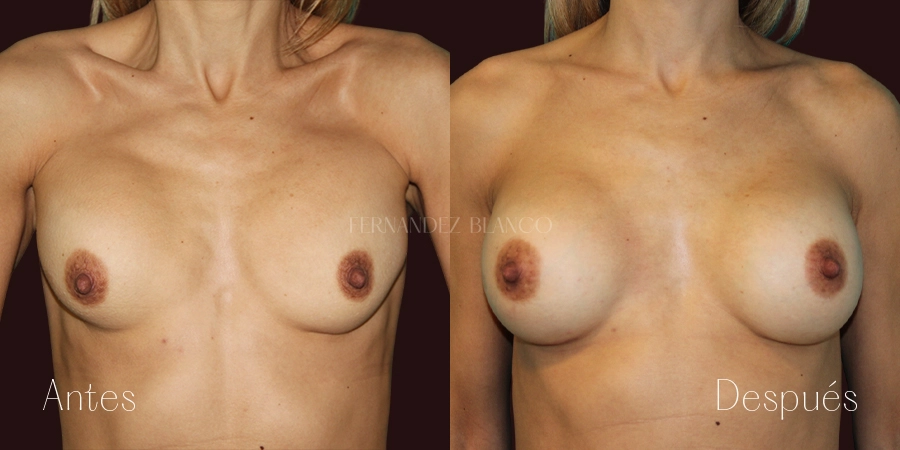
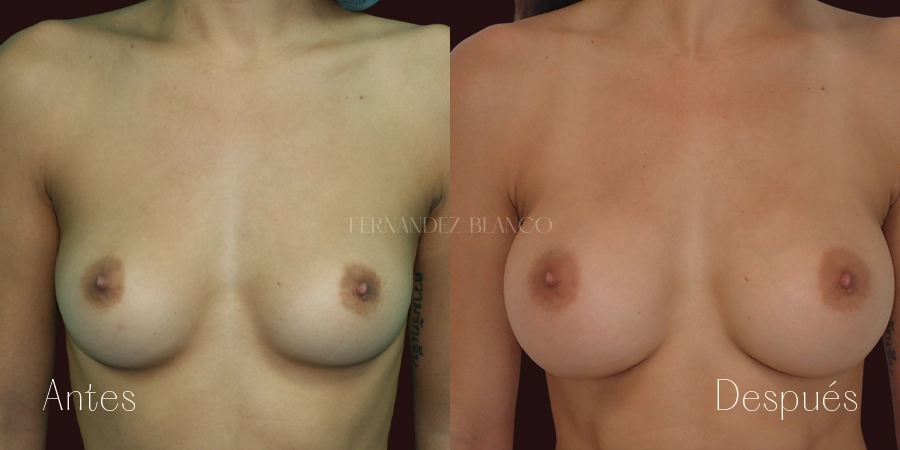
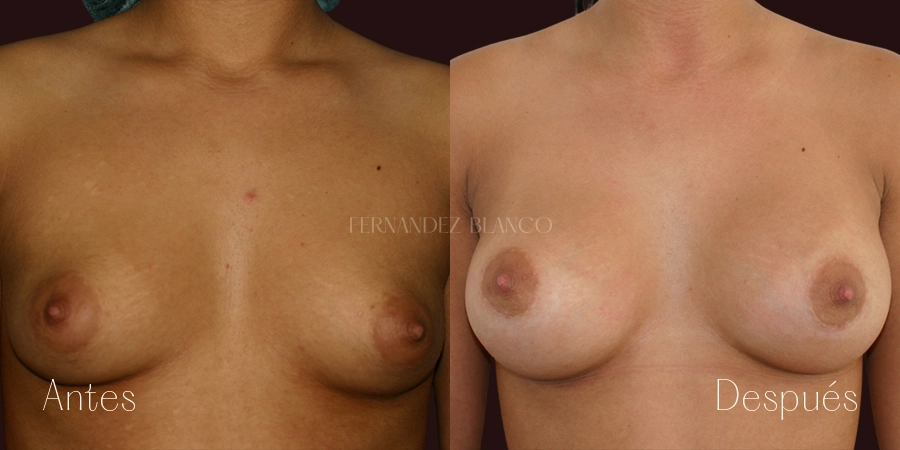
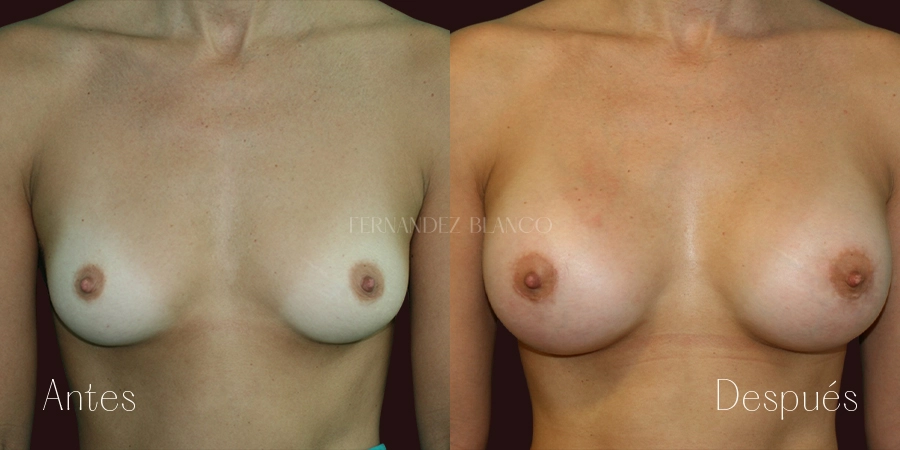
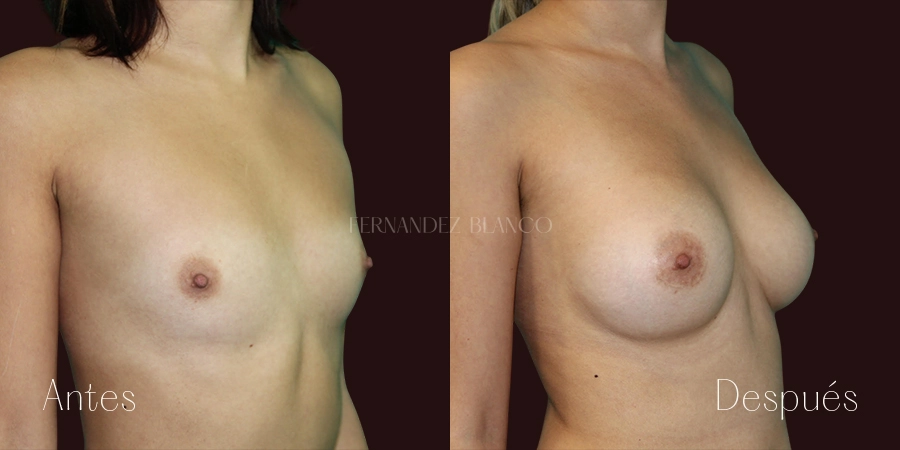
A breast augmentation consists of correcting the volume and shape of the breast, which is small, with a prosthesis implant. There are different surgical techniques, and it will be the surgeon who will advise the patient on the most appropriate based on the shape of the breasts, anatomy and skin quality.Lipofilling or Breast Lipotransfer
Lipofilling is the surgical procedure by which fat is extracted from one area of the body, processed and then injected into another region. Lipofilling is a useful technique to correct certain defects, such as filling the upper pole in some mastopexies with really good results or when the breast does not have enough skin coverage (very thin breast) and does not properly cover the prosthesis, so that the irregularities of the same could be felt and the defects are disguised with this procedure.Breast Asymmetry
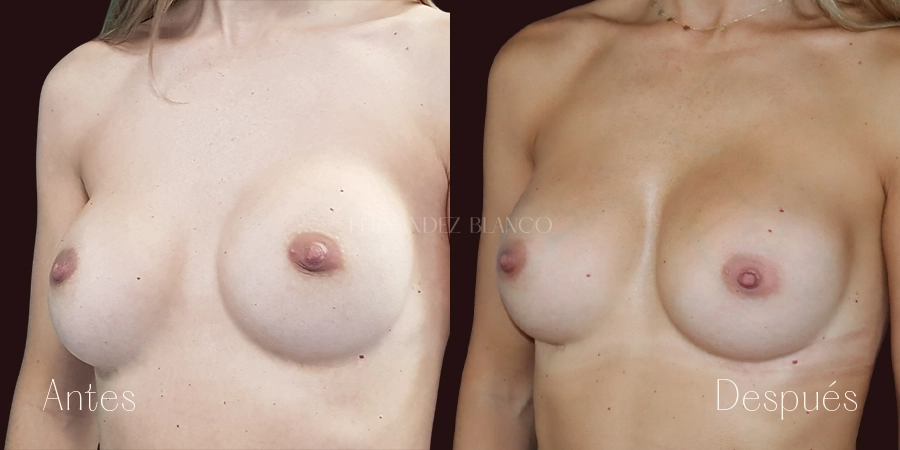
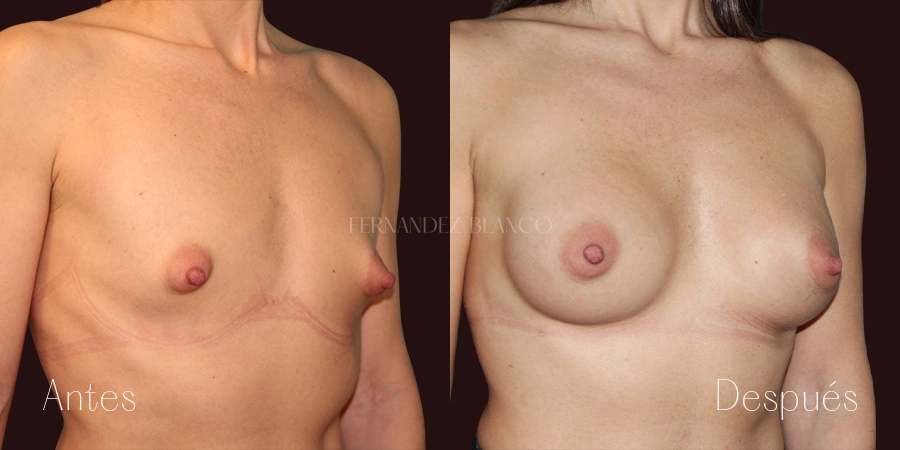
Practically all women have breast asymmetry, a peculiarity that can be manifested either by a difference in size, shape or location of the nipples. But there are cases where the asymmetry is too noticeable. There are different techniques to solve this asymmetry and together with the surgeon specialist will choose the most appropriate for each case.Breast reduction
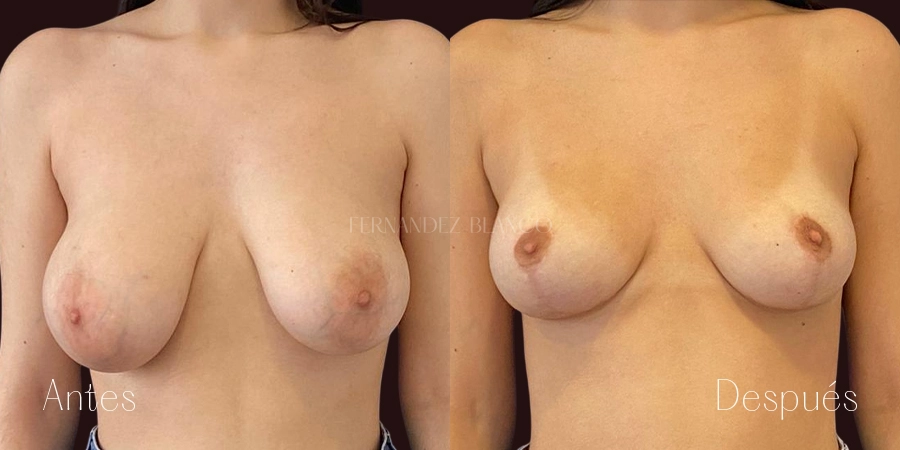
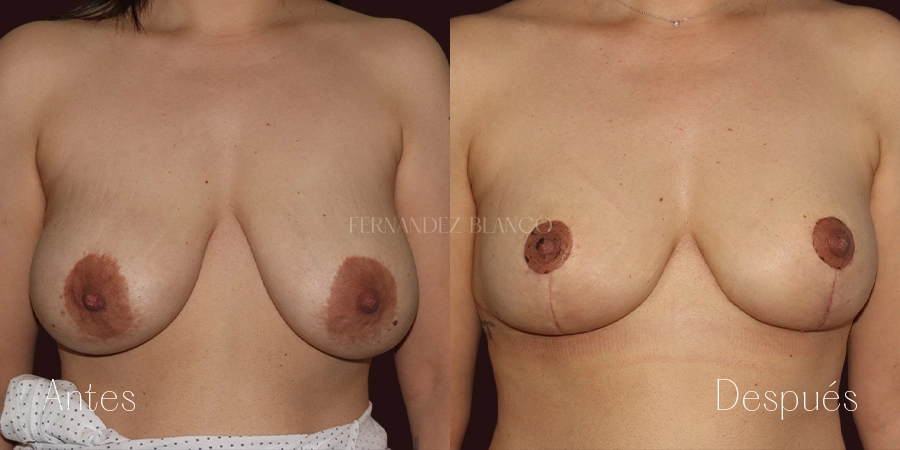
Breast reduction is the surgical intervention that allows the reduction of breast size, achieving a smaller and firmer breast. In addition to the aesthetic purpose, breast reduction also corrects physical problems, since for many women the excess breast volume is the source of discomfort such as back pain and even self-esteem.Mastopexy or breast lift
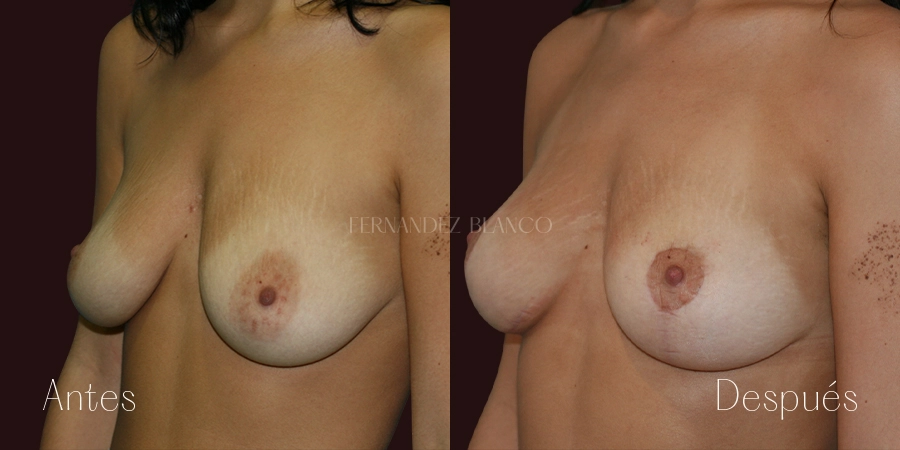
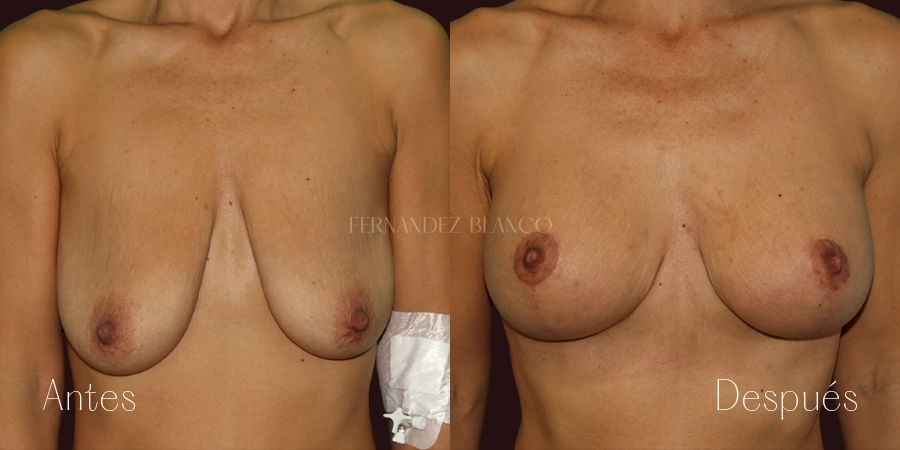
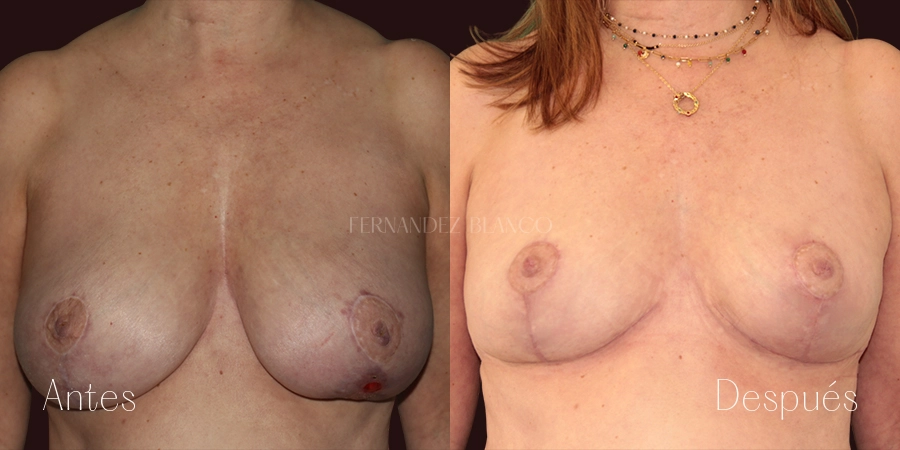
Mastopexy is the surgery performed to correct breast sagging without altering the volume. A breast is considered sagging when the nipple is below the mammary fold. This type of patient has an excess of skin, usually thin skin, without elasticity and with the presence of stretch marks. Breast sagging is independent of breast volume and can occur in small volumes and with breast hypertrophy.Sinmastia or United Implants
Sinmastia is the anatomical alteration consisting of the loss of the intermammary fold, that is, the lack of separation between the breasts. This anomaly usually involves the displacement of the areolas towards the outside causing a very out of normal result. Although synmastia may be due to a congenital defect (existence of a membrane that joins the two breasts), it is usually the result of a breast prosthesis implant performed incorrectly.Capsular Contracture
Capsular contracture or breast encapsulation is a complication of augmentation mammoplasty. Although the capsule formation is a natural process, it can contract abnormally over the implanted prosthesis, oppressing it and producing different problems. The patient feels discomfort, hardness to the touch, stiffness and in some cases pain.Prosthesis explantation
Prosthesis explantation consists of the definitive removal of the breast prosthesis. It is an intervention that has gone from being something unusual to being performed frequently. The aspect that most worries patients before this type of surgery is the result. This will depend on many factors, such as if the surgery is recent, the prosthesis could be removed even by the same scar and the chest would have its usual appearance. If, on the other hand, the implants are old, due to the distension of the skin, other treatments (such as mastopexy) will be required to provide aesthetic beauty.TYPE OF ANESTHESIA
General anesthesia
RECOVERY TIME
1 month
DEFINITIVE RESULT
1 to 3 months
Cases
Process
INTERVENTION
- Periareolar, around the areola
- Combination of periareolar and vertical cut, for moderate cases.
- Periareolar, vertical and transverse in the mammary sulcus (inverted "T") for important cases.
POST-OPERATORY
Informative Videos
Frequently Asked Questions
Is breastfeeding possible?
If in the process of insertion of breast implants, the ducts that connect the mammary gland through the nipple to the outside are respected, breastfeeding is not interrupted.
How long after breastfeeding should I wait for surgery?
We recommend that the patient undergo surgery 6 months after she has stopped breastfeeding, so that the breast is not swollen, is not active and the rate of capsular contracture complication decreases.
Difference between smooth and rough surface prosthesis
Initially breast prostheses were all smooth and at this point, it was thought that roughening the surface of the prosthesis would reduce the rate of capsular contracture. But over time it has been seen that this does not solve the problem. It has even been discovered that with rough prostheses another type of capsular contracture is created, where the organism wraps the rough prosthesis and attaches a layer of tissue that converts the rough prosthesis into a smooth one and then generates the same capsule. Then it is a double capsule.
How to choose between anatomical or round breast prosthesis?
It is a decision that must be evaluated according to the circumstances. When the patient has normal characteristics with a moderate breast (i.e. has a little breast) and normal skin coverage, it is preferable to use the round prosthesis. When we need to increase the lower pole, because the patient has little breast tissue or tuberous breast, sometimes it is better to place anatomical prosthesis. But not always because sometimes this result can be achieved with a high profile prosthesis. With a correct placement a high profile achieves a good result.
Location of the prosthesis in front of or behind the muscle?
In front of the muscle: This is a more anatomical plane. If the patient has good coverage, the prosthesis in front of the muscle has excellent results. In addition, when the patient contracts the muscle, the prosthesis is not altered. It has its indications. What happens is that the capsular contracture rate is higher in front of the muscle than behind the muscle. Behind the muscle: The prosthesis is placed in those cases in which the patient has little breast tissue. The prosthesis is not completely covered by the muscle, only the upper pole, the lower part always remains under the subcutaneous cellular tissue. In the case of folds of the prosthesis this will be hidden under the muscle and as we have mentioned before, in this technique of implantation, the rate of contracture is lower, it also seems that in this position the loss of sensitivity is lower.
Does breast prosthesis favor the development of breast cancer?
The relationship between breast cancer and prostheses has been investigated without revealing any link between the two and the implantation of a breast prosthesis does not increase the risk of breast cancer at all. Surgeons at cancer centers frequently use breast prostheses in reconstructive surgery.
Breastfeeding after correction of breast asymmetry
Since the implant is placed behind the gland, the correction of breast asymmetry by this procedure seems to have no influence on lactation.
Who needs a breast prosthesis explant?
This procedure is indicated for all those women who decide to remove their breast prostheses. The reasons why a patient decides to remove the implants and not replace them are usually: Complications with the implants, poor aesthetic result and changes in aesthetic taste.
What does the breast look like after the implants are removed?
With little time from the first surgery it is possible to return to the patient's natural silhouette, but if they are old implants, the breast is a little emptier, due to the effect of atrophy of the breast tissue and the distension of the skin for a long time, and it will be necessary to use complementary procedures.
Is it possible to remove the prosthesis and replace it with autologous fat?
We can use autologous fat to increase breast volume and repair defects caused by tissue atrophy. But the volume achieved is never as important as that obtained with breast implants.
Is breastfeeding possible after breast reduction?
In cases where the reduction is significant (from 500 gr.), the patient cannot be assured that she will be able to maintain lactation.
Is sensitivity lost after breast surgery?
A reduction in sensation is normal in the first few months when the sensation is like numb or "corked" skin. Unless there is some complication, with time, the sensitivity recovers in full.
Can scars be removed with laser?
There is no technique to erase scars. They can be improved with different procedures including laser.
For more information,
request an appointment
Our medical team will advise you on the treatment that best suits you, the surgical process, the possible risks and everything you need to know before facing such an important decision.
*Surgeries are performed in a duly authorized hospital.