Cirugía de Pecho
¿EN QUÉ
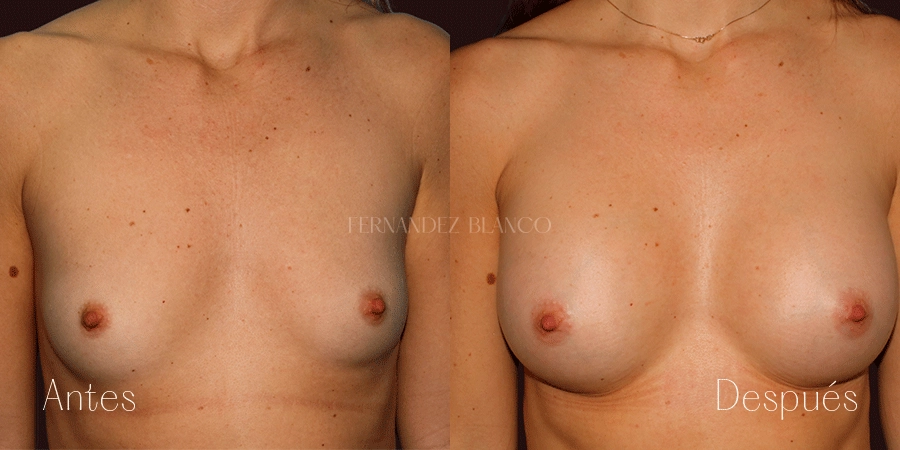
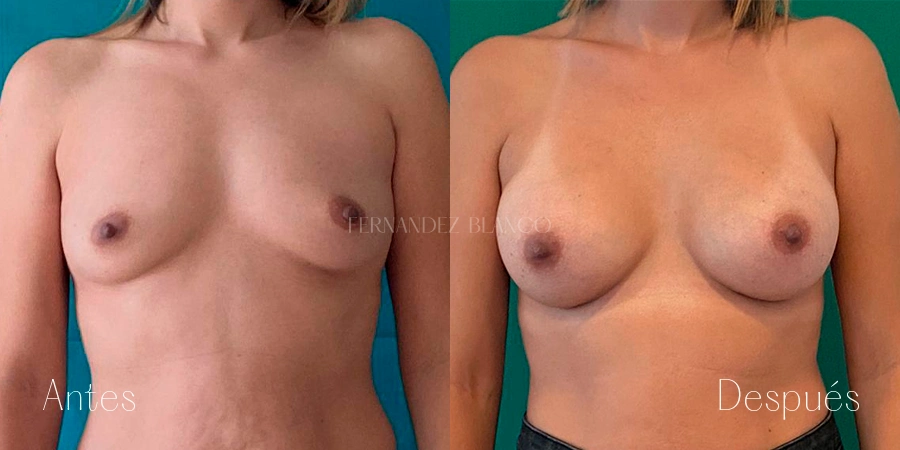
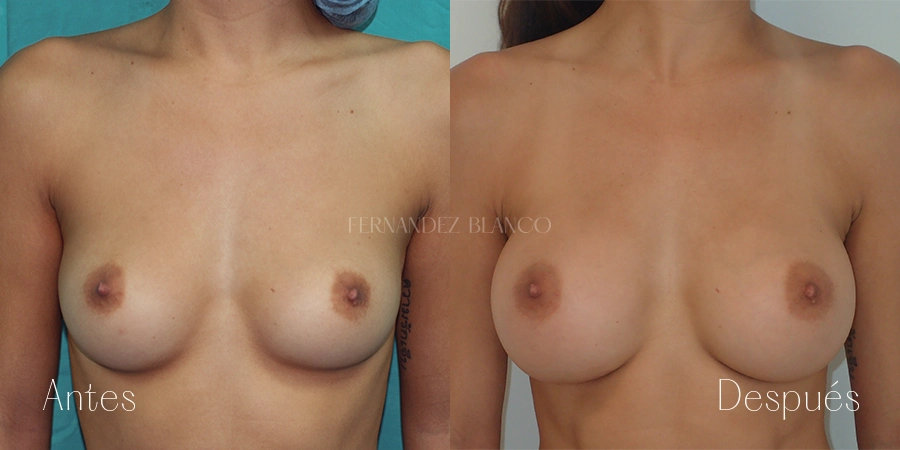
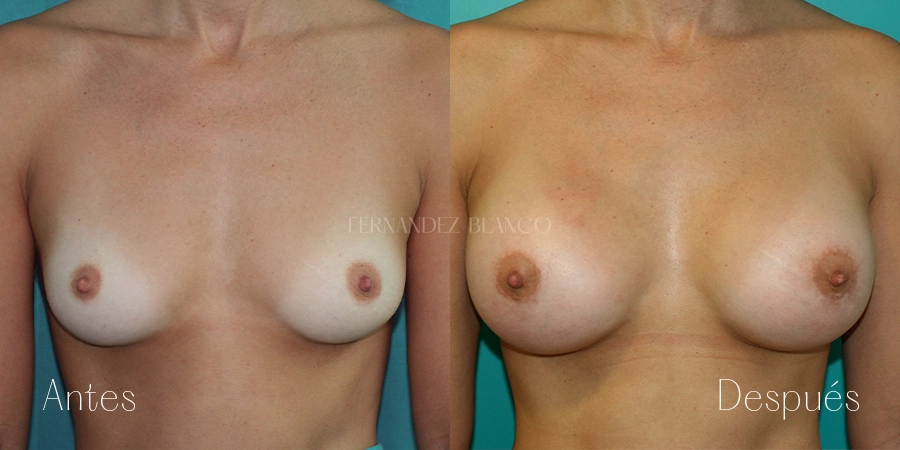
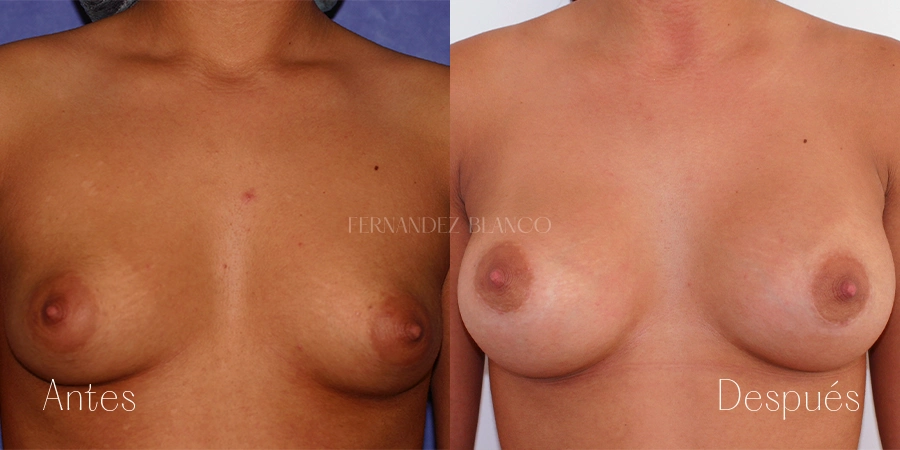
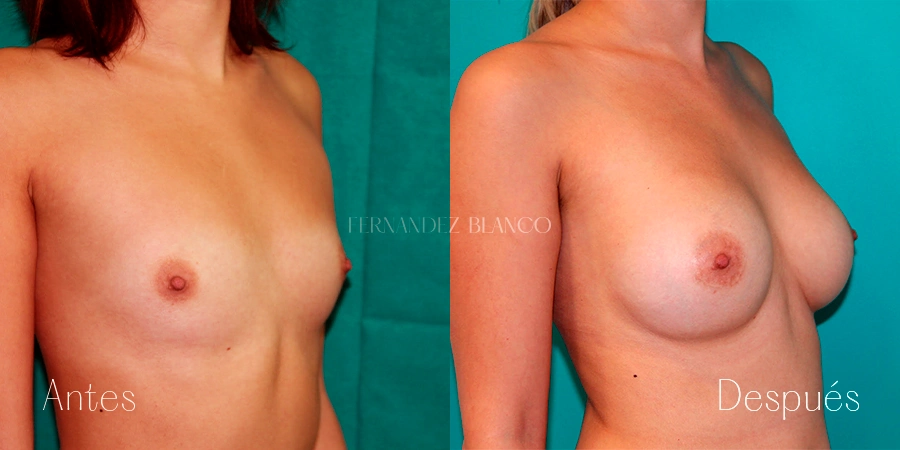
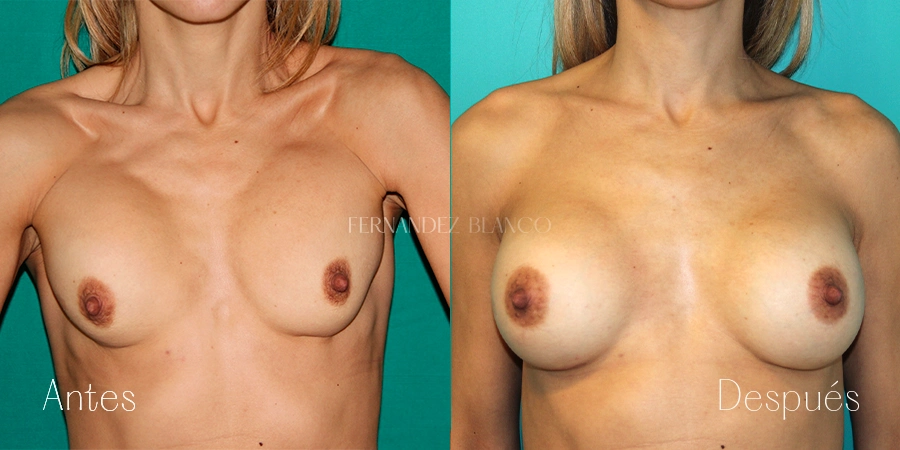
Aumento de pecho
Un aumento de pecho consiste en corregir el volumen y la forma de la mama, que es pequeña, con un implante de una prótesis. Existen distintas técnicas quirúrgicas, y será el cirujano quien aconsejará a la paciente sobre la más adecuada basándose en la forma de los pechos, la anatomía y la calidad de la piel.
Lipofilling o Lipotransferencia de mamas
El lipofilling es el procedimiento quirúrgico, por el cual se extrae grasa de una zona del cuerpo, se procesa y se inyecta posteriormente en otra región. El lipofilling es una técnica útil para corregir determinados defectos, como por ejemplo, rellenar el polo superior en algunas mastopexias con unos resultados realmente buenos o cuando la mama no tiene suficiente cobertura cutánea (mama muy delgada) y no cubre correctamente la prótesis, de manera que podrían palparse las irregularidades de la misma y los defectos se disimulan con este procedimiento.
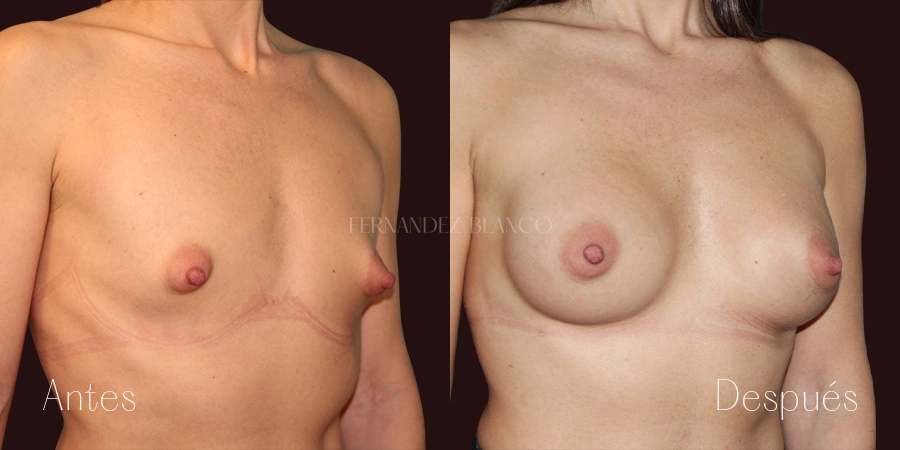
Asimetría Mamaria
Prácticamente la totalidad de las mujeres tienen asimetría mamaria, una peculiaridad que puede manifestarse ya sea por una diferencia de tamaño, en la forma o la ubicación de los pezones. Pero existen casos donde la asimetría es demasiado notable. Existen distintas técnicas para solucionar esta asimetría y junto con el cirujano especialista se escogerá la más adecuada para cada caso.
Reducción de pecho
La reducción de pecho es la intervención quirúrgica que permite la disminución del tamaño de la mama, consiguiendo un pecho más pequeño y firme. Además de la finalidad estética, la reducción de senos corrige también problemas físicos, dado que para muchas mujeres el exceso de volumen mamario es origen de molestias como dolor de espalda e incluso en el autoestima.
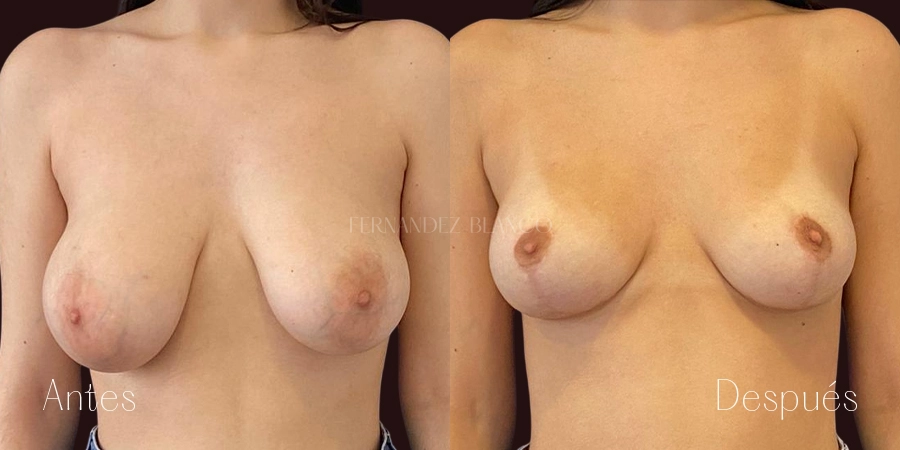
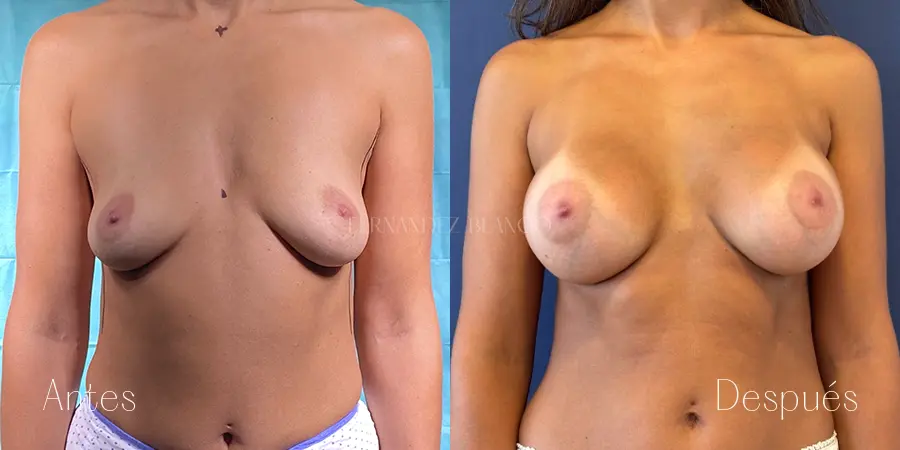
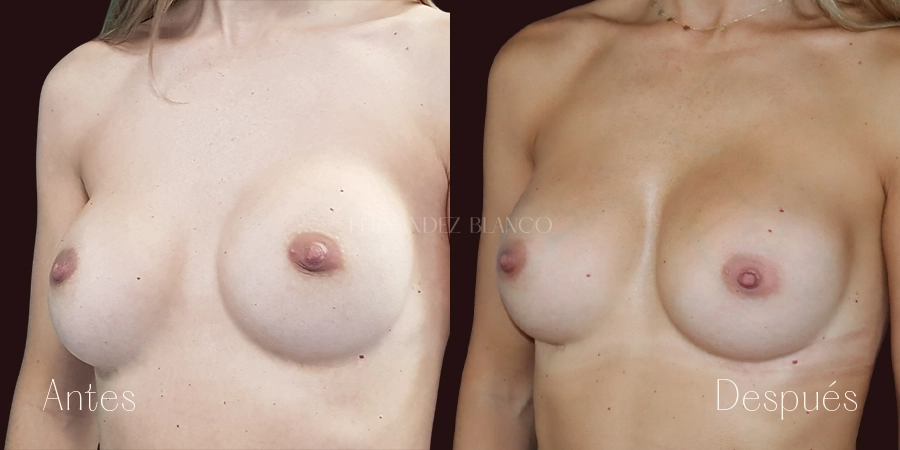
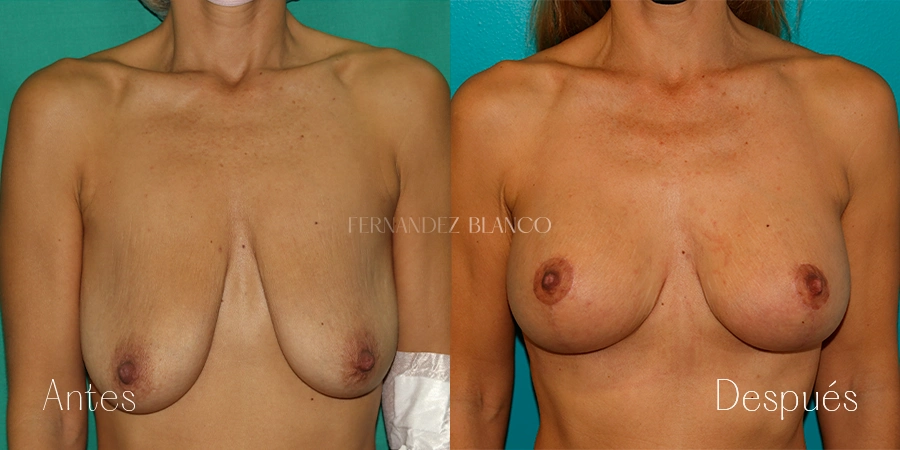
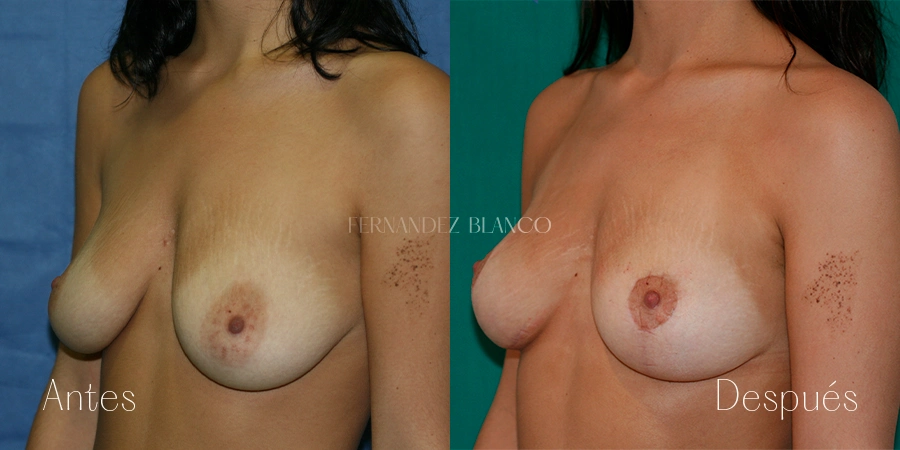
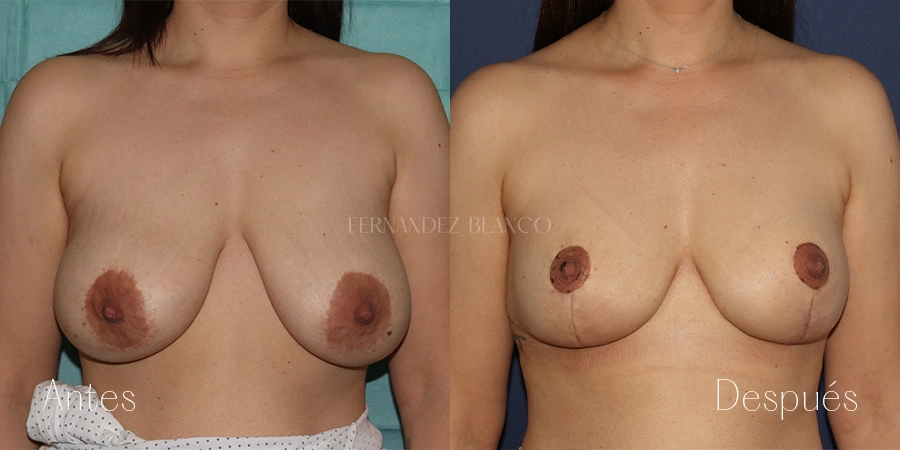
Mastopexia o levantamiento de pecho
La Mastopexia es la cirugía que se realiza para corregir la caída mamaria sin alterar el volumen. Se considera que una mama está caída cuando el pezón está por debajo del surco mamario. Este tipo de pacientes, tienen un exceso de piel, normalmente piel fina, sin elasticidad y con la presencia de estrías. La caída de la mama es independiente del volumen mamario pudiendo producirse en volúmenes pequeños y con hipertrofia de mama.
Sinmastia o Implantes Unidos
Se denomina sinmastia a la alteración anatómica consistente en la pérdida del surco intermamario, es decir, a la falta de separación entre las mamas. Esta anomalía suele suponer el desplazamiento de las areolas hacia el exterior provocando un resultado muy fuera de la normalidad.
Si bien la sinmastia puede deberse a un defecto congénito (existencia de una membrana que une las dos mamas) lo habitual es que sea consecuencia de un implante de prótesis de mama realizado incorrectamente.
Contractura Capsular
La contractura capsular o encapsulamiento mamario es una complicación de la mamoplastia de aumento. Aunque la formación de cápsula es un proceso natural, esta puede llegar a contraerse de manera anómala sobre la prótesis implantada, oprimiéndolo y produciendo distintos problemas. La paciente siente incomodidad, dureza al tacto, rigidez y en algunos casos dolor.
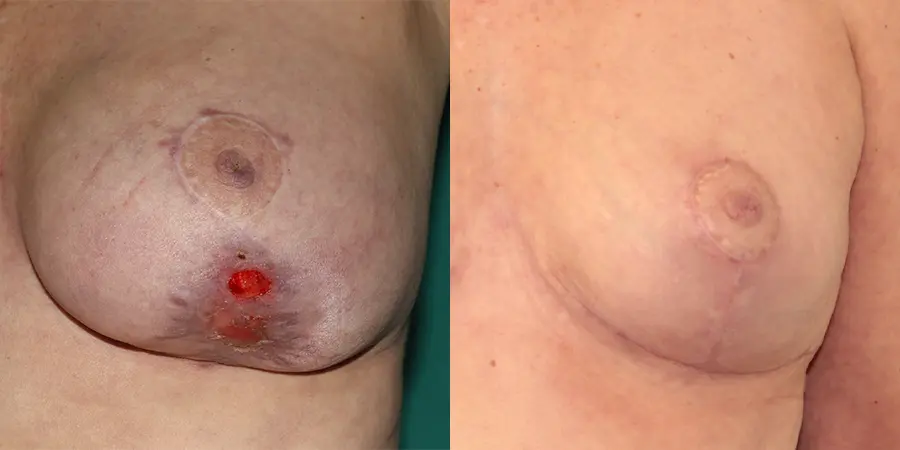
Explante de prótesis
La explantación de prótesis consiste en la extracción definitiva de la prótesis mamarias. Es una intervención que ha pasado de ser algo inusual a realizarse con frecuencia. El aspecto que más preocupa a las pacientes ante este tipo de cirugía es el resultado. Esto dependerá de muchos factores, como por ejemplo si la cirugía es reciente, la prótesis podría extraerse incluso por la misma cicatriz y el pecho volvería a tener su aspecto habitual. Si por el contrario son unos implantes antiguos, por la distensión de la piel, se requerirán otros tratamientos (como la mastopexia) para otorgarle belleza estética.
TIPO DE ANESTESIA
Anestesia general
TIEMPO DE RECUPERACIÓN
1 mes
RESULTADO DEFINITIVO
1 a 3 meses
Casos
Proceso
INTERVENCIÓN
Existen distintos tipos de disposición de las incisiones:
- Periareolar, alrededor de la areola
- Combinación de periareolar y corte vertical, para casos moderados.
- Periareolar, vertical y transversal en el surco mamario (en "T" invertida) para casos importantes.
La elección de la técnica depende del criterio del cirujano y de las características del seno a operar: edad, calidad de piel y volumen a reducir.
En cualquier caso, hay que procurar que las cicatrices sean lo más finas posibles, y que no soporten tensión.
POSOPERATORIO
La inflamación, los hematomas y la molestia al levantar los brazos son frecuentes al principio.
Es conveniente prever una convalecencia y una baja de trabajo aproximadamente de 8 a 10 días y es aconsejable esperar uno o dos meses para retomar una actividad deportiva.
Vídeos Informativos
Preguntas Frecuentes
¿Es posible la lactancia?
Si en el proceso de inserción de los implantes de mama, se respetan los conductos que conectan la glándula mamaria a través del pezón con el exterior, la lactancia no se interrumpe.
¿Cuánto tiempo después de dar el pecho debo esperar para la cirugía?
Recomendamos que la paciente se opere 6 meses después de haber dejado la lactancia, de manera que el pecho no se encuentra inflamado, no está activo y la tasa de complicación de contractura capsular disminuye.
Diferencia entre prótesis de superficie lisa y rugosa
En un inicio las prótesis de mama eran todas lisas y llegados a este punto, se pensó que haciendo rugosa la superficie de la prótesis se reduciría la tasa de contractura capsular. Pero con el tiempo se ha visto que esto no soluciona el problema.
Incluso se ha descubierto que con las prótesis rugosas se crea otro tipo de contractura capsular, donde el organismo envuelve la prótesis rugosa y le adhiere una capa de tejido que convierte la prótesis rugosa en lisa y luego genera la misma cápsula. Luego es cápsula doble.
¿Cómo decantarse por la prótesis de mama anatómica o redonda?
Es una decisión que hay que valorar en función de las circunstancias.
Cuando el paciente tiene características normales con un pecho moderado (es decir tiene un poco de mama) y una cobertura cutánea normal, es preferible usar la prótesis redonda. Cuando necesitamos aumentar el polo inferior, porque la paciente tiene poco tejido mamario o mama tuberosa, a veces es mejor colocar prótesis anatómicas. Pero no siempre porque a veces se puede conseguir este resultado con una prótesis de perfil alto. Con una colocación correcta un perfil alto consigue un buen resultado.
Ubicación de la prótesis ¿por delante o por detrás del músculo?
Delante del músculo: Se trata de un plano más anatómico. Si el paciente tiene una buena cobertura, la prótesis delante del músculo tiene unos resultados excelentes. Además cuando la paciente contrae el músculo, la prótesis no se altera. Tiene sus indicaciones. Lo que ocurre es que la tasa de contractura capsular es mayor delante del músculo que detrás del músculo.
Detrás del músculo: Se coloca la prótesis en aquellos casos en los que la paciente tiene poco tejido mamario. La prótesis no queda totalmente cubierta por el músculo, solo el polo superior, la parte inferior siempre queda debajo del tejido celular subcutáneo. En el caso de pliegues de la prótesis esto quedará oculto bajo el músculo y como hemos mencionado anteriormente, en esta técnica de implantación, la tasa de contractura es menor.También parece que en esta posición la pérdida de sensibilidad es menor.
¿Favorece la prótesis mamaria a la aparición de cáncer de mama?
La relación entre el cáncer de mama y las prótesis se ha investigado sin poner en evidencia ningún vínculo entre los dos y el implante de una prótesis mamaria no aumente para nada el riesgo de cáncer de mama. Los cirujanos de centros anticancerosos utilizan frecuentemente las prótesis mamarias en la cirugía reconstructiva.
Lactancia tras la corrección de la asimetría mamaria
Dado que el implante se coloca detrás de la glándula, la corrección de la asimetría mamaria por este procedimiento parece no tener influencia en la lactancia.
¿Quién necesita un explante de prótesis de mama?
Este procedimiento está indicado para todas aquellas mujeres que decidan retirarse las prótesis de mama. Los motivos por los que una paciente decide retirarse los implantes y no sustituirlos suelen ser: Complicaciones con los implantes, mal resultado estético y cambios en el gusto estético.
¿Cómo queda el pecho después de retirar los implantes?
Con poco tiempo desde la primera cirugía se puede conseguir volver a la silueta natural de la paciente, pero si son implantes antiguos, la mama queda un poco más vacía, debido al efecto de la atrofia del tejido mamario y la distensión de la piel durante mucho tiempo, y serán necesario utilizar procedimientos complementarios.
¿Es posible retirar la prótesis y suplantarla por grasa autóloga?
Podemos utilizar la grasa autóloga para aumentar el volumen mamario y reparar defectos producidos por la atrofia de los tejidos. Pero el volumen que se consigue nunca es tan importante como el que obtenemos con los implantes mamarios.
¿Es posible la lactancia tras una reducción de pecho?
En los casos en que la reducción es importante (a partir de 500 gr.), no se puede asegurar a la paciente que pueda mantener la lactancia.
¿Se pierde la sensibilidad después de una cirugía de pecho?
Es normal una reducción de la sensibilidad en los primeros meses en los que la sensación es como de piel adormecida o “acorchada”. A menos que exista alguna complicación, con el tiempo, la sensibilidad se recupera en su totalidad.
¿Se puede eliminar las cicatrices con láser?
No existe ninguna técnica para borrar las cicatrices. Se pueden mejorar con diferentes procedimientos entre los que se incluye el láser.
Infórmate,
pide una cita
Nuestro equipo médico te asesora sobre el tratamiento que mejor se adapte a ti, el proceso quirúrgico, los posibles riesgos y todo lo que necesitas saber antes de afrontar una decisión tan importante.
*Las cirugías se realizan en un hospital debidamente autorizado.